Care for Gum Problems Treatments in Woodbury
Understanding Gum Disease
Recognizing the Signs and Protecting Oral Health
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a chronic condition that affects the gums and the bone supporting the teeth. In its early stage, gingivitis, symptoms may include redness, swelling, and bleeding gums. When left untreated, gum disease can progress to periodontitis, causing the gums to pull away from the teeth, leading to bone loss, tooth mobility, and eventually tooth loss.
Gum disease often develops gradually and may not cause noticeable discomfort in the early stages. While it is more common in adults, children and teens can also develop gum disease, particularly when oral hygiene is inconsistent. Early diagnosis and ongoing care play an important role in maintaining healthy gums and supporting long term oral health.
Common Gum Disease Concerns
Changes in gum health can develop gradually and may not always cause discomfort in the early stages. Symptoms such as bleeding, inflammation, or gum recession can indicate underlying periodontal concerns that require evaluation. Identifying these signs early allows for timely care and helps support healthy gums and long term oral health.
Bleeding Gums
Bleeding during brushing or flossing may be an early sign of gum inflammation and should be evaluated.
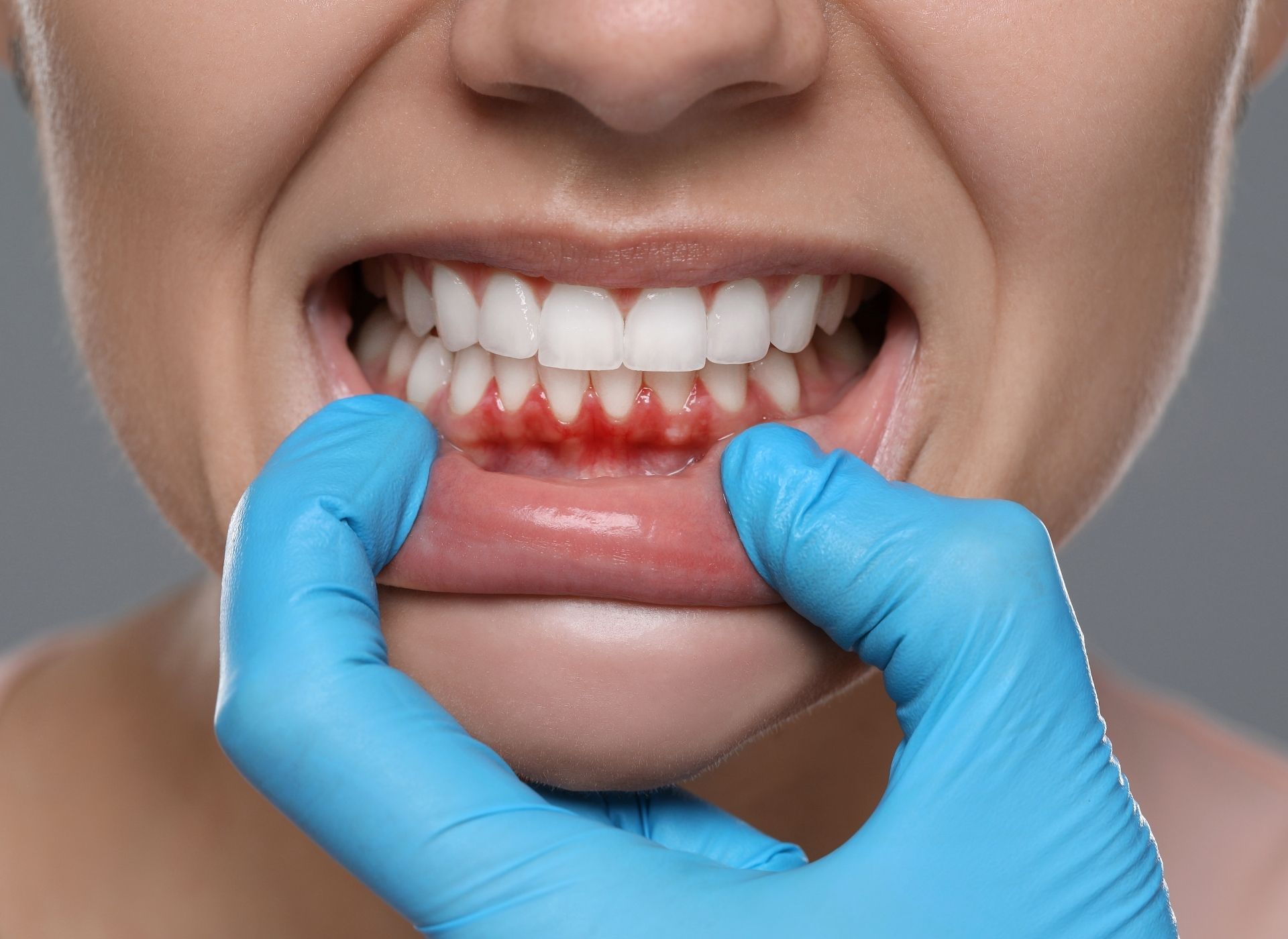
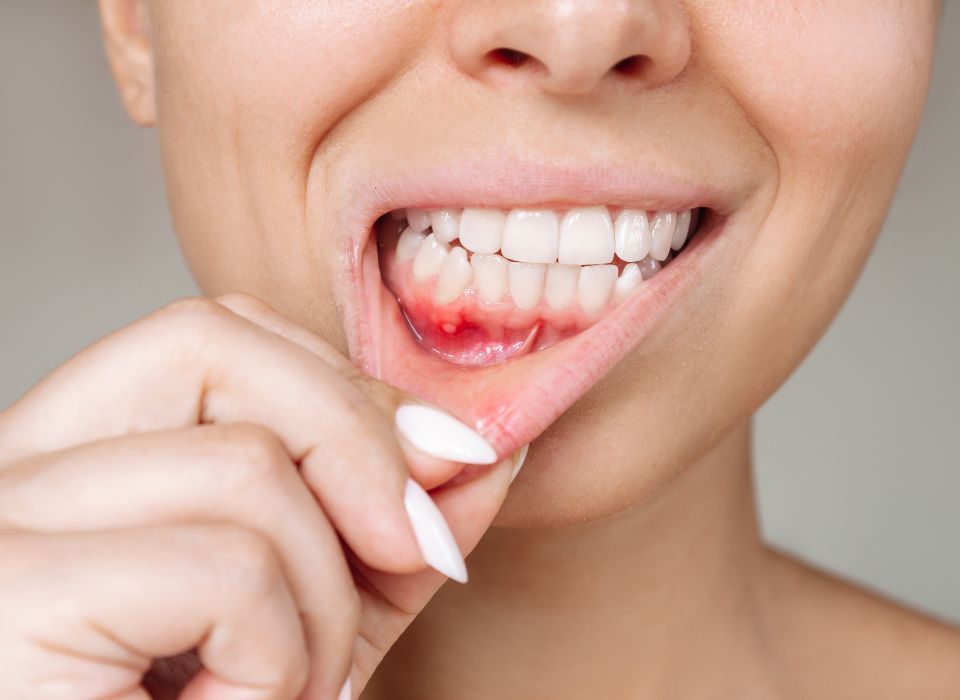
Periodontitis
Advanced gum disease that affects the supporting bone and tissues around the teeth.
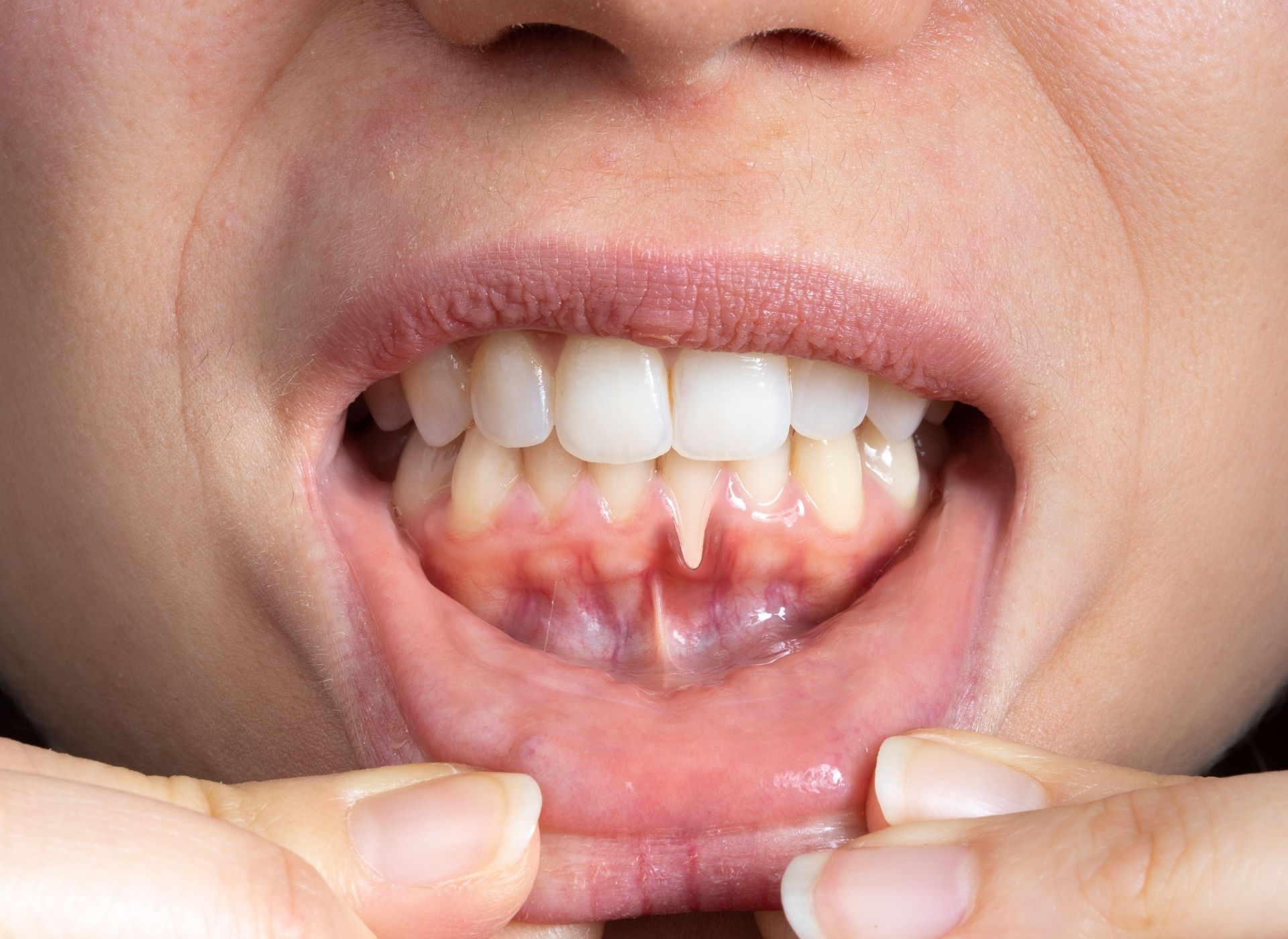
Gum Recession
A condition where the gums pull away from the teeth, exposing the roots and increasing sensitivity.
Managing Gum Disease Through Ongoing Care
Early Detection and Consistent Treatment
Gum disease and tooth decay are among the most common threats to oral health. Many patients are unaware they have gum disease until it becomes more advanced. Regular dental exams allow changes in gum health to be identified early, when treatment is often more effective and less invasive.
Treatment recommendations depend on the stage and severity of the condition and may focus on reducing inflammation, controlling infection, and supporting gum and bone health. Consistent home care and routine dental visits are essential in managing gum disease and helping prevent further progression.





